The best list of material design color palettes, tools, and resources
Содержание:
- Buttons
- How to alternate row color in Google Sheets
- Configuration¶
- How to change the color of a range of cells
- Выбор цвета элемента
- Material Design Websites
- Customization
- Color
- How to remove color from cells in Google Sheets
- Shape
- Widget styles and attributes
- Typography
- How to change cell color in Google Sheets
- Text Fields
- Customization¶
- Немного истории
- How to change border color in Google Sheets
- Использование цветов в UI
- Активные цвета
- Palette colors
- Анимация в Material Design
- How to remove alternating colors
- Bottom Navigation
- Build a Material Theme
- More resources
Buttons
Material Buttons include four main variants that all inherit from the base style, each with an optional style suffix: raised (default, no suffix), unelevated (), outlined () and text (). All button variants use the theme attribute for their typography styles.
The key attributes for customizing these styles are as follows:
- : The tint color applied to the button background. The default enabled color is transparent for text buttons and for all other variants.
- : The tint color applied to an optional button icon. The default enabled color is for text buttons and for all other variants.
- : The color of the button touch ripple. The default color is for raised/unelevated buttons and for outlined/text buttons.
- : The color of the stroke around the button background. The default color is for outlined buttons and transparent for all other variants.
- : The width of the stroke around the button background. The default value is 1dp for outlined buttons and 0dp for all other variants.
- : The shape appearance of the button background. The default value is .
The base button style (used by the widget class) can be customized and applied globally like so:
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.MaterialComponents.Light"> ... <item name="materialButtonStyle">@style/AppButton</item></style><style name="AppButton" parent="Widget.MaterialComponents.Button"> <item name="backgroundTint">?attr/colorSecondary</item></style>
The result can be observed in our playground screen:
Customized Button widget styles
How to alternate row color in Google Sheets
In some cases you may want to color every other row in your spreadsheet, and this can be done in a much easier way than by manually selecting every other line before coloring.
To alternate row color in Google Sheets, select the range that you want to apply alternating colors to, open the «Fill color» menu, click «Alternating colors…», customize the options for styling, and then click «Done».
(If you want, you can also select the header or even the entire sheet)
If you prefer, you can also open the alternating colors menu without selecting a range first, and then type the range that you want to color in the «Apply to range» field. If you select the range before opening the menu, you will see that the «Apply to range» field will already be filled in.
When styling alternating colors, you can select a default style, or you can also specify which colors that you want to use.
You can also select whether or not you want there to be a special color for the header/footer.
If the color does not begin on the row that you want, for example if you want the color to be on even rows instead of odd rows… you can either adjust your source range by one row, or flip the colors assigned to «Color 1» and «Color 2» in the menu.
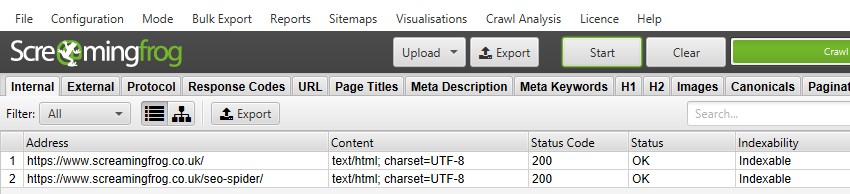
In this example the range that we are applying alternating colors to is A2:D9.
Configuration¶
Color palette
Color scheme
Source · Default:
Material for MkDocs supports two color schemes: a light mode, which is just called , and a dark mode, which is called . The color scheme can be set via :
Click on a tile to change the color scheme:
Primary color
Source · Default:
The primary color is used for the header, the sidebar, text links and several other components. In order to change the primary color, set the following value in to a valid color name:
Click on a tile to change the primary color:
Accent color
Source · Default:
The accent color is used to denote elements that can be interacted with, e.g. hovered links, buttons and scrollbars. It can be changed in by choosing a valid color name:
Click on a tile to change the accent color:
Color palette toggle
Source · Default: none
It’s also possible to offer a list of color palettes to the user, each of which can include a , and color each. The user can toggle between those color palettes:
The following fields must be set for each toggle:
-
Default: none · Required – This field must point to a valid icon path referencing any icon bundled with the theme, or the build will not succeed. Some popular combinations:
- + – +
- + – +
- + – +
- + – +
-
Default: none · Required – This field is used as the toggle’s attribute and should be set to a discernable name to improve accessibility.
System preference
Source · Default: none
In order to automatically set the color palette to the user’s system preference, a media query can be set as part of the field next to the toggle definition in :
When the user first visits your site, the media queries are evaluated in the order of their definition. The first media query that matches selects the default color palette.
Accessibility – not all color combinations work well
With 2 (color schemes) x 21 (primary colors) x 17 (accent color) = 714 combinations, it’s impossible to ensure that all configurations provide a good user experience (e.g. yellow on light background). Make sure that the color combination of your choosing provides enough contrast and tweak CSS variables where necessary.
How to change the color of a range of cells
Now let’s select multiple cells to color, or in other words we will select a range of cells to color.
To color a range of cells in Google Sheets, select the range of cells that you want to color, open the «fill color» menu, then select the color that you want.
In this example we will color the range A1:D1 to make the cells in the header stand out. (Notice that only 4 cells are selected here, as opposed to a whole row being selected which we will go over in the next example)
To do this simply select the range A1:D1, then open the fill color menu as previously demonstrated at the top of the article, and select your desired color (cornflower blue in this example).
To select a range of cells (A1:D1), use one of the following methods to select multiple cells:
- Click and drag the cursor from Cell A1 to cell D1, or…
- Hold the «ctrl» key on the keyboard while individually clicking the cells A1, B1, C1, and D1 or…
- Select cell A1 and then while holding the «shift» key on the keyboard, then press the right arrow key on the keyboard 3 times or…
- Select cell A1 and then while holding the «shift» key on the keyboard, click cell D1
Выбор цвета элемента
Чтобы изменить фоновый цвет страницы, используйте поле Заливка на панели Свойства, когда элементы не выбраны.
Можно изменять цвет контура и заливки элементов с помощью инструментов для работы с цветом. Чтобы настраивать цвета, используйте панели «Цвет» и «Свойства» или инструменты «Контур» и «Заливка» на панели инструментов.
С помощью панели «Цвет»
- Нажмите на элемент, для которого нужно выбрать цвет.
- Нажмите на образец цвета возле параметра Заливка или Граница в верхней части панели «Цвет».
- Выберите цвет на цветовой панели или в палитре образцов цветов.
С помощью панели «Свойства»
- Нажмите на элемент, для которого нужно выбрать цвет.
- В разделе Стиль панели Свойства нажмите на образец в поле Цвет заливки или Цвет границы. Откроется цветовая панель.
- Выберите цвет на цветовой панели, в палитре образцов цветов или в рабочей области с помощью инструмента «Пипетка».
С помощью инструмента «Заливка»
- Выберите инструмент Заливка на панели инструментов или нажмите клавишу F. Если на панели инструментов есть инструмент «Контур» или «Градиент» , нажмите и удерживайте его, чтобы выбрать инструмент «Заливка» во всплывающем меню.
- Выберите цвет, нажав на значок с образцом или используя панель «Цвет».
- Наведите указатель мыши на элемент, для которого нужно выбрать цвет. Вокруг него появится зеленый контур.
- Нажмите на элемент.
С помощью инструмента «Контур»
- Нажмите и удерживайте инструмент Заливка на панели инструментов, затем во всплывающем меню выберите инструмент Контур . Если на панели инструментов отображается инструмент «Градиент», нажмите и удерживайте его кнопку, чтобы выбрать инструмент «Контур» во всплывающем меню. Также можно нажать клавишу K.
- Настройте контур:
- Чтобы выбрать цвет контура или границы, нажмите на значок с образцом на панели инструментов.
- Укажите толщину границы (для большинства элементов) или контура (для объектов типа «Линия» и «Овал») на панели настроек инструмента.
- Выберите стиль границ в раскрывающемся меню Стиль на панели настроек инструмента.
- Наведите указатель мыши на элемент, границы которого нужно изменить. Вокруг него появится зеленый контур.
- Нажмите на элемент.
Material Design Websites
1. Google
When it comes to Material Design, how can we not mention Google? It’s the best practice of its own material design guidelines. The material design style is characterized by the clean typography and simple layout that is easy to understand so the user can focus on content.
2. WhatsApp
WhatsApp is a timely communication tool loved by people around the world, implements the concept of material design in its web design and mobile App design very well. In terms of colors, WhatsApp did not use a very colorful palette for its main colors, opting for a more serene mix of gray and green.
These Material Design color tools and resources will help you move to the next step in practicing building your website or App.
Actually, it’s not that hard. To create a website or App that incorporates Material Design, you only need a material design style prototyping tool. Here I give my vote to Mockplus as it has the unique advantage of both in website prototype design and mobile App prototype design. Combining the built-in material design components of Mockplus with the material design color scheme I summarized for you above, designing a Material design style application or website is no longer a difficult task.
Customization
You may override the default palette values by including a palette object as part of your theme.
If any of the:
palette color objects are provided, they will replace the defaults.
The palette color value can either be a object, or an object with one or more of the keys specified by the following TypeScript interface:
Using a color object
The simplest way to customize an intention is to import one or more of the provided colors
and apply them to a palette intention:
Providing the colors directly
If you wish to provide more customized colors, you can either create your own color object,
or directly supply colors to some or all of the intention’s keys:
As in the example above, if the intention object contains custom colors using any of the
«main», «light», «dark» or «contrastText» keys, these map as follows:
- If the «dark» and / or «light» keys are omitted, their value(s) will be calculated from «main»,
according to the «tonalOffset» value. - If «contrastText» is omitted, its value will be calculated to contrast with «main»,
according to the «contrastThreshold» value.
Both the «tonalOffset» and «contrastThreshold» values may be customized as needed.
The «tonalOffset» value can either be a number between 0 and 1, which will apply to both light and dark variants, or an object with light and dark variants specified by the following TypeScript type:
A higher value for «tonalOffset» will make calculated values for «light» lighter, and «dark» darker.
A higher value for «contrastThreshold» increases the point at which a background color is considered
light, and given a dark «contrastText».
Note that «contrastThreshold» follows a non-linear curve.
Color
Color attributes consist mainly of primary, secondary, error, surface and background colors, along with their respective secondary variants and “on” colors. Some of these have been reused from the AppCompat themes (eg. , and ):
- : The primary brand color of your app, used most predominantly in theming
- : A lighter/darker variant of your primary brand color, used sparingly in theming
- : The color used for elements displayed on top of your primary colors (eg. Text and icons, often white or semi-transparent black depending on accessibility)
- : The secondary brand color of your app, used mostly as an accent for certain widgets that need to stand out
- : A lighter/darker variant of your secondary brand color, used sparingly in theming
- : The color used for elements displayed on top of your secondary colors
- : The color used for errors (often a shade of red)
- : The color used for elements displayed on top of your error color
- : The color used for surfaces (i.e. Material “sheets”)
- : The color used for elements displayed on top of your surface color
- : The color behind all other screen content
- : The color used for elements displayed on top of your background color
These colors can be added to your app theme like so:
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.MaterialComponents.Light"> <item name="colorPrimary">#212121</item> <item name="colorPrimaryVariant">#000000</item> <item name="colorOnPrimary">#FFFFFF</item> <item name="colorSecondary">#2962FF</item> <item name="colorSecondaryVariant">#0039CB</item> <item name="colorOnSecondary">#FFFFFF</item> <item name="colorError">#F44336</item> <item name="colorOnError">#FFFFFF</item> <item name="colorSurface">#FFFFFF</item> <item name="colorOnSurface">#212121</item> <item name="android:colorBackground">@color/background</item> <item name="colorOnBackground">#212121</item></style><color name="background">#FAFAFA</color>
Note 1: Hex color codes are not currently supported for , hence why a color resource was used.
Note 2: Use and attributes to theme system bars.
The result can be observed in our playground screen:
Playground screen with global color attributes customized
A great way to quickly preview the appearance of primary/secondary colors is to use the Material Color Tool.
How to remove color from cells in Google Sheets
Removing color from cells, is in most cases almost exactly the same process as adding color.
To remove color from cells in Google Sheets, select the cells/rows/columns that you want to remove color from, open the «Fill color» menu, and then click «Reset». You can also simply click the color white if you prefer.
Another way to remove color from cells, including any color that is applied through conditional formatting or alternating colors, is to clear the formatting of selected cells by doing the following:
- Select the cells that you want to clear color/formatting from
- Click the «Format» menu in the toolbar
- Click «Clear formatting»
(Using «Clear formatting» will clear ALL/ANY formatting from the cells)
Now you know lots of different ways to color your spreadsheets, so that you can make your finished work visually appealing and very easy to read!
Shape
Shape attributes refer to the general form of each surface and widget in your app. When you consider that these components can be of varying width/height and be raised/unelevated/outlined, this reduces down to one aspect of customization… Corners.
Material Components corners can either be part of the rounded (default) or cut and have a to customize the size. A treatment can be applied to all corners or a subset. The shape theme attributes reference styles:
- : For small components, such as Buttons and Chips
- : For medium components, such as Cards
- : For large components, such as Bottom Sheets
The Material Components widgets will use these styles as per the Material guidelines.
If you wish to customize the Material Components shape appearance styles, you would do so like this:
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.MaterialComponents.Light"> ... <item name="shapeAppearanceSmallComponent">@style/AppShapeAppearance.SmallComponent</item> <item name="shapeAppearanceMediumComponent">@style/AppShapeAppearance.MediumComponent</item></style><style name="AppShapeAppearance.SmallComponent" parent="ShapeAppearance.MaterialComponents.SmallComponent"> <item name="cornerFamily">cut</item> <item name="cornerSize">8dp</item></style><style name="AppShapeAppearance.MediumComponent" parent="ShapeAppearance.MaterialComponents.MediumComponent"> <item name="cornerFamily">cut</item> <item name="cornerSize">8dp</item></style>
The result can be observed in our playground screen:

Playground screen with global shape attributes customized
Widget styles and attributes
While global theming covers the majority of our needs, there are times when we may wish to customize the attributes of individual widgets. We will explore the styles (and relevant attributes) of common widgets and how these can be referenced in your Material Components theme.
Typography
Type attributes adhere to the Material Type System in terms of text typeface, weight, size, case and letter spacing. The attributes reference styles that implement (and are named after) the various type scales:
- : Light, 96sp
- : Light, 60sp
- : Regular, 48sp
- : Regular, 34sp
- : Regular, 24sp
- : Medium, 20sp
- : Regular, 16sp
- : Medium, 14sp
- : Regular, 16sp
- : Regular, 14sp
- : Regular, 12sp
- : Regular, 14sp, all caps
- : Regular, 12sp, all caps
The Material Components widgets will use these styles as per the Material guidelines.
You would typically want to keep the default weight, size, case and letter spacing for each style. However, a custom typeface can really make your app stand out. One might assume this requires overriding each and every one of these attributes. Thankfully, this can be done in a far more concise way by adding the following attributes to your app theme:
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.MaterialComponents.Light"> ... <item name="fontFamily">@font/roboto_mono</item> <item name="android:fontFamily">@font/roboto_mono</item></style>
These attributes reference an XML Font or a Downloadable Font that you’ve added to your folder and will apply a custom typeface to every widget and text style in your app. There was certainly a time when it wasn’t this easy on Android!
If you do, however, wish to customize one of the Material Components text appearance styles, you would do so like this:
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.MaterialComponents.Light"> ... <item name="textAppearanceButton">@style/AppTextAppearance.Button</item></style><style name="AppTextAppearance.Button" parent="TextAppearance.MaterialComponents.Button"> ... <item name="android:textAllCaps">false</item></style>
The results can be observed in our playground screen:
Playground screen with global type attributes customized
Lastly, Google Fonts is a great place to start if you’re looking for free-to-use, custom typefaces (which happen to work really well with Downloadable Fonts too).
How to change cell color in Google Sheets
First, let’s change the color of a single cell. When referring to changing the color of a cell itself, we are talking about changing the background color of that cell.
To color a cell in Google Sheets, select the cell that you want to color, open the «fill color» menu, then select the color that you want.
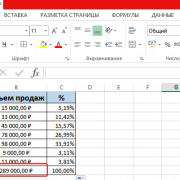
Notice that in this example, in cell C6, the assignment grade is 32.71%. Let’s say that we want to manually mark this cell red, to make it stand out.
To do this simply click/select cell C6, then open the «Fill Color» menu, then select the color red.
(See the top of this article for visual instructions on selecting color from the palette)
Text Fields
Material Text Fields include two main variants. As a result of porting the pre-existing AppCompat and classes, there are in fact two base styles: and . The variants have a style suffix and include filled box (default, ) and outlined box (). All text field variants use the standard text appearance for input and the theme attribute for “helper” text (labels, errors, counters, etc.).
The key attributes for customizing the styles are as follows:
- : The mode of the box background, which can be either , or .
- : The color of the text field background. The default enabled color is for filled box text fields and transparent for outlined box text fields.
- : The color of the stroke around the text field background. The default color is (in default state) for outlined box text fields and is ignored for filled box text fields.
- //: Various colors for different “helper” text sub-components.
- : The shape appearance of the text field background. The default value is .
The base text field style (used by the widget class) can be customized and applied globally like so:
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.MaterialComponents.Light"> ... <item name="textInputStyle">@style/AppTextField</item></style><style name="AppTextField" parent="Widget.MaterialComponents.TextInputLayout.FilledBox"><item name="boxBackgroundColor">@color/text_field_background</item></style>
Note: is a that uses and the same alpha values as the default .
The result can be observed in our playground screen:
Customized Text Field widget styles
Customization¶
Custom colors
Source · Difficulty: easy
Material for MkDocs implements colors using CSS variables (custom properties). If you want to customize the colors beyond the palette (e.g. to use your brand-specific colors), you can add an and tweak the values of the CSS variables.
Let’s say you’re YouTube, and want to set the primary color to your brand’s palette. Just add:
See the file containing the color definitions for a list of all CSS variables.
Custom color schemes
Source · Difficulty: easy
Besides overriding specific colors, you can create your own, named color scheme by wrapping the definitions in the , which you can then set via as described in the section:
Additionally, the color scheme defines all of it’s colors via color functions and deduces its colors from the CSS variable. You can tune the theme with:
Немного истории
Сегодня мы привыкли к тому, что интерфейсы Google выглядят и работают примерно одинаково. Но так было не всегда. Еще десять лет назад приложения для Android, десктопная почта и мобильный веб были похожи друг на друга не больше, чем крот на пианино.
В 2011 году в Google решили, что с этим пора что-то делать, и действительно что-то сделали. А именно — унифицировали свои продукты, создали единый стиль для приложений Android Holo. Только вот они снова оказались разными.
В результате пользователи все так же терялись при переключении между мобильным и десктопным интерфейсами: выглядели они по-разному, управлялись тоже — проблема оставалась.
Gmail.com (Kennedy)
Gmail for Android (Holo)
How to change border color in Google Sheets
You may also find certain situations where you want to change the color of borders in Google Sheets.
Most likely you will want to do this to simply change the shade of grey/black of borders, but in this example I have used the color red to make the lines stand out.
To change border color in Google Sheets, you must first select the cell or range of cells that you want to modify, then open the «Borders» menu in the toolbar, then open the «Border color» menu, and then you must apply the type of border that you want to see. If you do not apply / re-apply borders, changing the line color will not take effect.
In this example we are going to color the borders of the cells in the range A2:D9 red. (I have also made the lines thicker here to make the color stand out more in the image)
To do this, select the range A2:D9, open the «Borders» menu, and then open the «Border color» menu, and then select the color red.
Использование цветов в UI
Выберите палитру
Чтобы ограничить свою цветовую выборку выберите три оттенка из основной палитры и один акцентный цвет из вспомогательной палитры.
Пример основной цветовой палитры
Пример вспомогательной палитры
Используйте непрозрачность для текста, иконок и разделителей
Чтобы сообщить пользователю, насколько важна определенная информация относительно остального текста, вы можете изменять непрозрачность текста.
Темный текст на светлом фоне
Белый текст на темном фоне
Если темный текст расположен на светлом фоне, непрозрачность основного текста должна составлять 87%. Вспомогательный текст, расположенный ниже в визуальной иерархии, должен иметь непрозрачность 54%
Текстовые подсказки для пользователей, вроде тех, что расположены в текстовых полях и в метках, имеют еще меньшую визуальную важность и непрозрачность 26%
| Темный текст (#000000) | Непрозрачность |
| Основной текст | 87% |
| Вспомогательный текст | 54% |
| Подсказки (текстовые поля, метки) | 26% |
Светлый текст на темном фоне
Значения в таблице отражают относительную значимость светлого текста на темном фоне.
| Светлый текст (#FFFFFF) | Непрозрачность |
| Основной текст | 100% |
| Вспомогательный текст | 70% |
| Подсказки (текстовые поля, метки) | 30% |
Текст на цветном фоне
Для случаев расположения белого или черного текста на цветном фоне ознакомьтесь с этими , в которых указаны оптимальные значения контраста и альфа-канала.
Прочие элементы
Прочие элементы, такие как иконки и разделители, тоже выигрывают, если в качестве величины цвета используют шестнадцатеричное значение черного или белого, поскольку это гарантирует, что они дадут желаемый результат на фоне любого цвета.
Панели инструментов и панели состояния
Панели инструментов и более крупные цветные блоки должны использовать основной оттенок (500) главного цвета вашего приложения. Панель состояния должна использовать более темный оттенок (700) вашего основного цвета.
Смелое использование цвета в больших полях поощряется в UI. Различные элементы в UI могут использовать различные части вашей цветовой темы.
Акцентный цвет
Используйте акцентный цвет для вашей основной кнопки действия и компонентов, таких как переключатели или слайдеры.
В плавающей кнопке действия используется акцентный цвет.
Переключатель, использующий акцентный цвет.
Правильно.
В основном тексте используйте акцентный цвет только для привлечения внимания к веб-ссылке.
Неправильно.
Не используйте акцентный цвет в качестве цвета основного текста.
Правильно
Используйте акцентный цвет для вашей основной кнопки действия и компонентов, таких как переключатели или слайдеры.
Неправильно.
Не используйте акцентный цвет для панелей своего приложения или для крупных цветных участков. Избегайте использования одного и того же цвета для плавающей кнопки действия и для фона.
Запасные акцентные цвета
Если выбранный вами акцентный цвет окажется слишком светлым или слишком темным для выбранного фона, то в качестве запасного варианта обычно используется более темный или светлый оттенок акцентного цвета. Если ваш акцентный цвет совершенно не подходит, используйте оттенок 500 вашего основного цвета на белом фоне. Если для цвета фона выбран оттенок 500 вашего основного цвета, используйте 100% белый или 54% черный.
Правильно
Если цветной фон окажется слишком светлым или слишком темным, используйте запасной акцентный цвет.
Неправильно.
Не используйте акцентный цвет на цветном фоне, если контраст недостаточно высок.
Активные цвета
Активные цвета контура и заливки представлены значками в нижней части панели инструментов слева. Цвет контура (цвет границы) обозначен незакрашенным значком.
На примере ниже выбраны цвета по умолчанию: белая заливка и черный контур.
Активные цвета применяются при использовании следующих инструментов:
- «Элемент»;
- «Перо» и инструменты добавления фигур;
- «Заливка» и «Контур».
Если выбран один элемент, активные цвета будут использоваться для его заливки и контура.
Активные цвета можно легко изменить с помощью кнопок над значками с образцами цветов:
- Стандартные цвета – позволяет вернуться к настройкам по умолчанию (белая заливка и черный контур).
- Поменять заливку и контур – меняет местами цвета заливки и контура (также можно нажать клавишу X).
Palette colors
A color intention is a mapping of a palette color to a given intention within your application.
The theme exposes the following palette colors (accessible under ):
- primary — used to represent primary interface elements for a user. It’s the color displayed most frequently across your app’s screens and components.
- secondary — used to represent secondary interface elements for a user. It provides more ways to accent and distinguish your product. Having it is optional.
- error — used to represent interface elements that the user should be made aware of.
- warning — used to represent potentially dangerous actions or important messages.
- info — used to present information to the user that is neutral and not necessarily important.
- success — used to indicate the successful completion of an action that user triggered.
If you want to learn more about color, you can check out the color section.
Анимация в Material Design
В отличие от Apple, у которых анимация несет преимущественно эстетическую функцию, Google делает ставку на UX и функциональность. В их рекомендациях анимации уделено гораздо больше внимания, а на конференциях то и дело им посвящаются доклады.
Основная идея анимации в Material Design — сделать пользовательский интерфейс выразительным и простым в использовании. Для этого она должна отвечать трем принципам.
Информативность
Анимация показывает пространственные и иерархические связи между элементами: какие действия доступны пользователю и что произойдет, если он выполнит одно из них.
Анимация фокусирует внимание на том, что важно, и не отвлекает от основного действия
Анимация выражает характер, индивидуальность и стиль каждого продукта.
Таким образом, с помощью анимации можно:
Показать пользователю, как элементы связаны друг с другом.
Показать, как выполнять разные действия.
3. Сделать вау-эффект
Добавить привлекательности, чтобы пользователь снова захотел взаимодействовать с продуктом.
И это только верхушка айсберга. Google действительно заставил мир пересмотреть отношение к анимации и сделал ее полноценной частью UX-дизайна. Можно искать недостатки в рекомендациях Material Design, но, думаем, не стоит совсем игнорировать значение анимации сегодня.
А вот забавное замечание об одном из положений Material Design — о том, что все предметы, выходящие из экрана, должны ускоряться
Ведущий разработчик Джон Шлеммер считает, что неважно, где именно они остановятся
«В руководстве по материальному дизайну Google, похоже, думают, что вы должны только ускоряться при выходе из экрана», — Паскаль Д’Сильва. Источник
Благодаря Material Design анимация сегодня — не просто эффектное дополнение дизайна, а полноценная его часть. Если вы все делаете правильно, движение оживляет ваш интерфейс и заставляет пользователей любить интерфейс. Научиться создавать крутые анимации можно на курсе «Анимация интерфейсов».
Курс «Анимация интерфейсов»
Вы сможете самостоятельно создавать любую анимацию в интерфейсах и эффективно доносить концепцию проектов до клиентов. Мы начнем с анимации простейших элементов, таких как иконки, и дойдем до создания полноценных кейсов и шоурилов.
- Живая обратная связь с преподавателями
- Неограниченный доступ к материалам курса
- Стажировка в компаниях-партнёрах
- Дипломный проект от реального заказчика
- Гарантия трудоустройства в компании-партнёры для выпускников, защитивших дипломные работы
How to remove alternating colors
At the bottom of this article I will go over how to remove color from cells in general, but let’s go over how to remove alternating colors specifically.
To remove alternating colors in Google Sheets, select the range that has color to remove, open the alternating color menu while (open the «Fill color» menu, then click «Alternating colors»), and then click «Remove alternating colors».
Alternating row color is a format that will remain even if you click «Reset» in the color menu. If you manually color a cell that already has alternating colors, you will see the color change to what you manually select, but the alternating color format will still be applied in the background unless you click «Remove alternating colors» as described above.
To remove alternating colors, after selecting the range that you want to remove color from, you can also open the «Format» menu, and then click «Clear formatting».
I’ll go over clearing formatting more below, but for now, note that this will remove ALL formatting from a cell.
Material Bottom Navigation includes two main variants that inherit from the base style, with an optional style suffix: surface (default, no suffix) and colored (). Bottom Navigation labels use the theme attribute for their typography styles.
The key attributes for customizing these styles are as follows:
- : The color of the bottom navigation background. The default color is for surface bottom navigation and for colored bottom navigation.
- /: The colors of bottom navigation item icons and labels. The default colors are /(selected) for surface bottom navigation and for colored bottom navigation.
- : A flag to set whether or not a translation animation should occur when selecting bottom navigation items. The default value is false.
The base bottom navigation style (used by the widget class) can be customized and applied globally like so:
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.MaterialComponents.Light"> ... <item name="bottomNavigationStyle">@style/AppBottomNavigation</item></style><style name="AppBottomNavigation" parent="Widget.MaterialComponents.BottomNavigation.Colored" />
The result can be observed in our playground screen:
Customized Bottom Navigation widget style
This is certainly not exhaustive. A more comprehensive list of all components and their attributes can be found in the Material Components for Android Docs.
Build a Material Theme
The Material Components for Android library includes a module that allows you to easily customize an existing Material Theme. It provides you with a set of XML files (/, and ) which include all of the necessary baseline theme attributes mentioned in this article. The values can be tweaked and previewed in a corresponding sample app. When you’re happy with the chosen values, the files can be dropped into a new/existing Android Studio project. A web version is also available on Glitch.
The “Build a Material Theme” sample app
More resources
- The source code for the Playground app used in this article can be found on GitHub
- “The Components of Material Design” — A great presentation by Cameron Ketcham and Gautham Sajith at Android Dev Summit 2018, covering a brief history of Material Design and how to use Material Components for Android
- “Designing and building a real Android app using Material Tools & Components” — A presentation I gave at Droidcon Kenya and DevFest South Africa 2018, covering how I designed and built Rugby Ranker using the Material Theme Editor Sketch Plugin, Material Gallery and, of course, Material Components for Android
- Material Design Codelabs