Настройка dd wrt в режиме клиент
Содержание:
- [edit] Secondary Router on a Separate Subnet
- [edit] Installable Packages
- [edit] Going Offline/Before Implementation
- Flashing Your Router with DD-WRT Firmware
- [edit] V24_pre_sp2 K24
- [edit] Why do I only get blank pages when I try to change a setting in the web interface and hit apply?
- [edit] Теперь начинается ответственная часть — перепрошивка!
- [edit] How do I read signal and noise ratings?
- [edit] Identifying Your DD-WRT Firmware
- [edit] Method 1: Flashing with Web GUI
- [edit] Переход в автономный режим / до перепрошивки
- Перепрошивка маршрутизатора
- [edit] Introduction
- [edit] Other Notes
- [edit] Диагностика
- [edit] Способ 1: использование веб-интерфейса маршрутизатора
- [edit] Roaming access
- [edit] Method 2: Flashing with TFTP
- [edit] Какие настройки безопасности беспроводной сети следует использовать дома?
- Внешние ссылки
- [edit] Приготовьтесь к автономной работе
- [edit] Other Notes
[edit] Secondary Router on a Separate Subnet
If you want a secondary router to be on a separate subnet from the primary, just hard reset the router and set the router’s IP to, e.g., 192.168.5.1 on the basic setup page. Then set security and SSID on the Wireless tab, hit Save then Apply, and finally plug the LAN cable from your primary to the WAN of the second router.
If you wish to be able to access your secondary router from devices on your primary LAN, enable Web GUI management in the Remote Access section of the Administration/Management page. You should then be able to access the secondary router by typing in its WAN IP. Setting up a static lease for the second router’s WAN interface in Services on the first router will allow you to always know where the second one is to access it. This is the usual router/gateway mode, which is NOT the main goal of this Wiki.
[edit] Installable Packages
|
|
[edit] Going Offline/Before Implementation
- Do NOT use a wireless connection to GUI upload firmware. Use a wired (LAN) connection.
- Disable any wireless adapters (see the ) on your system to ensure that none are used for the transfer.
- Recommended: AFTER you are offline, disable your anti-virus software, as as a false positive detection could interrupt the upload. Disable all firewalls and security (see Disable Security. Restore security measures before going back online.
Flashing Your Router with DD-WRT Firmware
Three methods of flashing are covered below: using the router’s online interface (Method 1), via TFTP (), and with the Command Line Interface ( — use this if wirelessly connected). The router model and/or location may dictate what you use.
[edit] V24_pre_sp2 K24
Особенности сборок
| Micro | Micro Plus | Micro Plus ssh | Mini | Mini Hotspot Kaid | Mini USB | Mini USB FTP | Nokaid | OpenVPN JFFS Small | STD | STD NoKaid | STD NoKaid NoHotspot NoStor | STD NoKaid USB | VOIP | VPN | Big | Mega | |
| Asterisk | |||||||||||||||||
| Bandwidth Monitoring | |||||||||||||||||
| Connection Warning Notifier | |||||||||||||||||
| EoIP Support | |||||||||||||||||
| Hotspot System | |||||||||||||||||
| HTTP Redirect | |||||||||||||||||
| HTTPS Support for Web Management | |||||||||||||||||
| Micro | Micro Plus | Micro Plus ssh | Mini | Mini Hotspot Kaid | Mini USB | Mini USB FTP | Nokaid | OpenVPN JFFS Small | STD | STD NoKaid | STD NoKaid NoHotspot NoStor | STD NoKaid USB | VOIP | VPN | Big | Mega | |
| Security Log | |||||||||||||||||
| SMTP Redirect | |||||||||||||||||
| Sputnik | |||||||||||||||||
| tcpdump | |||||||||||||||||
| Wifidog | |||||||||||||||||
Замечания
Сборки версии v24:
| filename | description |
|---|---|
| dd-wrt.v24_<type>_asus.trx | Web interface-версия для прошивки. Подробнее Flash Your Asus WL-500G Deluxe |
| dd-wrt.v24_<type>_generic.bin | Стандартная сборка для прошивки через web interface на всех поддерживаемых устройствах (включая Linksys WRT54G/GL/GS) и для прошивки Siemens SE505 через tftp с адресом 192.168.2.1 |
| dd-wrt.v24_<type>_wrt54g.bin | tftp версии для WRT54G. Вы МОЖЕТЕ прошить ими через веб-интерфейс, но только после применения микро-прошивки. Эти версии специально предназначены для прошивки через TFTP. (v5/v6 note: Since the WRT54G/GS v5-v6 uses a modified WAP54Gv3 once made ‘linux ready’, it will not accept these standard WRT54G/GS firmwares. You must use the ‘generic’ build for TFTPing to these units). |
| dd-wrt.v24_<type>_wrt54gs.bin | tftp версии для WRT54GS. Вы МОЖЕТЕ прошить ими через веб-интерфейс, но только после применения микро-прошивки. Эти версии специально предназначены для прошивки через TFTP. |
| dd-wrt.v24_<type>_wrt54gsv4.bin | tftp версии для WRTGSv4. Y Вы МОЖЕТЕ прошить ими через веб-интерфейс, но только после применения микро-прошивки. Эти версии специально предназначены для прошивки через TFTP. |
| dd-wrt.v24_<type>_wrtsl54gs.bin | tftp версии для WRTSL54GS. Вы МОЖЕТЕ прошить ими через веб-интерфейс, но только после применения микро-прошивки. Эти версии специально предназначены для прошивки через TFTP. |
| dd-wrt.v24_<type>_moto.trx | For initial Flash Your Motorola WR850G (Micro and Mini builds ONLY) |
где <type> заменяется на mini, std, voip, и т. д.
Для прошивки с оригинальной микропрограммы от Linksys, сначала прошейтесь версией mini через web interface.
После этого через веб-интерфейс новой прошивки можно прошить любую версию..
[edit] Why do I only get blank pages when I try to change a setting in the web interface and hit apply?
- If you have just updated the firmware, you probably need to reset the router! See Factory Defaults, Hard reset or 30/30/30 and Reset And Reboot.
- Clear out your web browser’s cache and/or try another browser.
- This is really odd, but try turning off your firewall temporarily while you’re updating the pages.
- This could also be a result of incompatibilities with Firefox. Try switching to an alternative browser (e.g. Internet Explorer or Konqueror) for the WebUI Management.
- If you’re on a Mac, try getting Chromium (i.e. Google Chrome for Mac). Safari and FireFox may not work at times, however Chromium worked for all my needs (including reliable firmware upgrade via web interface).
[edit] Теперь начинается ответственная часть — перепрошивка!
5. Необходимо выполнить процедуру 30/30/30 (3 раза по 30 секунд не отпуская держим нажатой кнопку RESET).
Что это за процедура? Она состоит в том, что нам нужно зажать кнопку RESET на корпусе работающего роутера и удерживать её 30 секунд. Прошло 30 секунд? НЕ отпускаем кнопку RESET и отключаем роутер от электросети на 30 секунд. Продолжаем держать кнопку и включаем роутер в розетку и ждем опять же 30 секунд.
Если Вы все сделали правильно, то после последних 30 секунд индикатор Power на лицевой панели будет равномерно мигать, а индикатор LAN 1, в который мы воткнули кабель, гореть постоянно.
Это значит, что роутер ждет получения прошивочных файлов. Не торопитесь! 🙂 Он будет ждать столько, сколько Вам будет нужно.
Итак, снова открываем консоль (надеюсь, Вы ее не закрыли? Если да, то наберите CMD, как показано выше).
6. В консоли пишем команду tftp -i 192.168.1.1 put (указать путь до файла wl500g-clear-nvram.trx) и нажимаем ENTER.
Не ошибитесь в написании пути к файлу. Теперь Вы поняли, почему нужно было сохранять файлы в корень? 😉 Что бы меньше было писать в консоли 😉
Получаем что-то типа этого:
ВНИМАНИЕ! После того, как Вы удачно «скормили» файл роутеру и он отрапортовал об этом (как на скриншоте), ЖДИТЕ НЕ МЕНЬШЕ 3 МИНУТ! Иначе роутер может прийти в негодность!
7. Подождав 3 минуты делаем процедуру 30/30/30 и снова наберем в консоли команду tftp -i 192.168.1.1 put, но только на этот раз укажите путь к файлу wl500g-recover.trx
Небольшая хитрость: не обязательно забивать команду и путь вручную. Достаточно удерживать клавишу курсора «вправо» и консоль наберет сама последнюю команду — Вам останется только подредактировать путь к файлу 🙂
Получим в итоге вот это:
Снова ждем 3 минуты, после чего снова делаем 30/30/30.
8. Теперь в консоли набираем ту же самую команду, но теперь «скормим» роутеру файл dd-wrt.v24_mini_asus.trx
Получаем:
Ждем 3 минуты и делаем 30/30/30.
9. Можете расслабиться — консоль нам больше не нужна 🙂 Выключите роутер секунд на 30 и снова включите его в розетку.
Зайдите через браузер в админку роутера, вбив в адресной строке браузера 192.168.1.1
Если вы пользуетесь агрессивными расширениями к браузеру, например NoScript или AdBlock в Firefox, то лучше их пока отключить.
Нас встретит вот такое приглашение придумать логин и пароль администратора. Не отказываемся от любезности и придумываем.
Перед нами прошитый роутер версией DD-WRT Mini. В принципе, если Вас устраивает функционал прошивки Mini (именно её мы и установили), то можете на этом остановиться и дальше не прошивать.
Но если хотите получить std_generic или даже mega_generic, то едем дальше.
10. Идем в вкладку Administration — Firmware Upgrade.
Выбираем чекбокс After flashing reset to — Reset to defolt setings
Ниже выбираем файл std_generic или mega_generic (смотря что Вы скачали и что хотите установить) и жмем Upgrade.
На скриншоте все понятно без лишних слов:
Начнется отсчет времени (будет задействован таймер).
ВНИМАНИЕ! Даже когда таймер дойдет до 0 не вздумайте что-то делать!!! Ждите! Роутер еще будет апгрейдиться и выдаст вот такое сообщение:
В бета-версиях прошивок бывает, что таймер закончил отсчет, а роутер все равно высвечивает просьбу подождать. Это не страшно. Подождите для уверенности минут 10 и выключите его из розетки секунд на 30. Он прошился, просто web-админка.
11. Прошились? Включаем роутер и на всякий случай сделаем еще разок 30/30/30. Затем выключить/включить роутер (с паузой в 30 секунд). Можно, в принципе, этого не делать, но для спокойствия все же лучше чуть-чуть напрячься.
13. Теперь можно залогиниться в 192.168.1.1 (в браузере) и роутер снова попросит придумать ему логин-пароль для администратора.
14. Лезем в настройки и настраиваем роутер как захочется 🙂 Ведь у нас чудесная прошивка DD-WRT!
Приятного роутинга 🙂
[edit] How do I read signal and noise ratings?
These numbers are given in decibels (dB) and are expressed as negative numbers. The more negative the number, the less strength it represents. Thus, -40 dB represents more strength than -70 dB. The values are logarithmic. A signal amplitude change of 3 dB is equivalent to a factor of two; 10 dB is a factor of ten.
Signal: (in dBm) A small negative number is good (-40 is good, -98 is bad)
Noise: (in dBm) A large negative number is good (-98 is good, -40 is terrible, -70 would be pretty bad in the real world)
SNR: (in dB) High is good (should be the same as difference between noise and signal, a difference of 20 would be great, a difference of 1 may barely work)
| SNR(dB) = Signal(dBm) — Noise(dBm) |
Signal Quality: High is good, somewhat like SNR but indexed to 100 with noise as the base, percentage of the best theoretical ideal quality in regards to your local-noise
Signal — Noise = SNR
-82 — -98 = 16
Signal / Noise * SNR = Signal Quality
-82 / -98 * 16 = 13.4%
Typically, noise will be -92 which means you should get a clean connection with a signal as low as -92. However, expecting to hold a good connection with a signal lower than -85 (e.g. -90), is expecting too much. The signal can be improved by -3 dB by doubling the power setting at the transmitting radio, e.g., 100 mW increased to 200 mW would improve your signal from -85 to -82. Antennas with increased gain will also help. Say you had the standard 3 dB antenna and changed it for a 12 dB antenna, that’s a 9 dB increase, so your signal would increase from -82 to -73 which would be an excellent signal, probably capable of 54 Mbps. Using the term excellent in terms of running a WISP, it would probably be only 3 bars on a 5 bar signal strength meter. Don’t worry if, as a WISP your signal quality is low, like 14%. It’s not really a problem since -82 is considered acceptable.
[edit] Identifying Your DD-WRT Firmware
- Use the brand-specific information in the Hardware-specific page to accurately identify which model you have. Start with the main brand heading (ie, «Linksys»). Use that information — instead of just going by what model you think you have — clock.
- Some newer routers are not supported by the latest stable release. Check the Supported Devices list for the minimum required DD-WRT version for your device. You may need to use an SVN or experimental build.
- For a comparison of the builds, see .
- Updating through the Web GUI (ie, the routers’s online interface) means you need to use the _generic version.
[edit] Method 1: Flashing with Web GUI
-
Reset your router
- This is probably not needed, but if the memory or nvram is almost full, a firmware update can brick it. Thus it is recommended at least until are familiar with the particular device.
- See Reset And Reboot and note the default IP address. If not listed on the router label see
- Perform a GUI reset (Administration->Factory Defaults in DD-WRT) or use an alternate method:
- Hard reset. WARNING: some devices should not use 30/30/30, including all ARM devices.
- Reset button: with the router running normally, hold the reset button until the lights flash (or up to 30 sec). Be careful when using this method! Research the functionality of your current firmware to be safe.)
-
Log in to the Web GUI
- Javascript is required for the Web interface. Try a different browser if having issues.
- Access the GUI via the router IP address. The default for DD-WRT and many devices is , or see . If the IP address is unknown, see Obtaining Router IP. If still having issues, .
- You will be prompted for username and password. (If your router already has a DD-WRT versions starting with 2006-Feb-28, the default username is root. Prior versions have a blank username by default. For Linksys firmware, the default username can be left blank or set to anything. For both DD-WRT and Linksys firmware, the default password is admin. Search online for other defaults on other routers).
-
Upload the Firmware
- NOTE: Multiple flashes may be needed if flashing from OEM firmware. See the .
- WARNING:DO NOT interrupt the setup while the router is being flashed and rebooted. Do not turn off the computer, close the web browser, or turn off the router during this process!
- This section is written for the DD-WRT GUI. An OEM firmware interface will be different. See .
- Click the «Administration»->»Firmware Upgrade» tab.
- Optional: select the option to Reset to Defaults after flashing (NOTE: this can cause flashing issues)
- Click the «Browse» button and select the DD-WRT .bin file you downloaded and confirmed.
- Click the «Upgrade» button and wait for a redirect page confirming successful upload.
- Now wait at least 5 minutes before clicking «Continue». This varies with the hardware.
- If flashed successfully you will now be able to access the DD-WRT web interface at .
-
Reset Again
- Do this only after you have confirmed that the firmware upgrade is working.
- This is required if flashing from OEM firmware! See the above section again.
- For DD-WRT upgrades, this should only be needed if making large build jumps, changing kernel version (e.g. 2.4 to 2.6 or 2.6 to 3.10), or if having issues. For the latter, reset, retest, and then search the forum before making a new post.
-
Possible Errors with Uploading Firmware
- If the DD-WRT web interface is not accessible after 10 minutes, try clearing the browser cache, renewing the IP address («ipconfig -renew» in a Windows command prompt window), another reset, or power cycle.
- Ping the router: a TTL=64 response indicates normal operation, while TTL=100 usually indicates a TFTP server awaiting firmware upload. TFTP usually only is available in the first couple seconds at power-up, and may time out if the file upload is larger than OEM versions. See Tftp_flash, and note only OEM firmware may work for TFTP, possible trailed builds.
- The firmware upload process may respond with «Upload Failed» if using the wrong file type, kernel, or size of DD-WRT (or may just brick). E.g. This may occur through the web GUI if you use a *wrt54g.bin version when you should have selected the generic version. It may also be that your router requires the mini version to be flashed before the full version. Ensure you have the right version, as described in the first section.
- See Recover from a Bad Flash or try a different internet browser to upload the firmware.
- If logging in fails with the default username/password, reset again.
[edit] Переход в автономный режим / до перепрошивки
- НЕ используйте для перепрошивки маршрутизатора компьютер, соединенный с ним по беспроводной сети Wi-Fi. Используйте проводное соединение (LAN).
- Отключите все беспроводные адаптеры в своей системе, чтобы убедиться, что ни один из них не используется для передачи данных. См. как это правильно сделать в статье .
- После отключения от интернета рекомендуется выключить на компьютере антивирус и брандмауэр, т.к. ложное срабатывание может прервать загрузку прошивки в маршрутизатор. См. статью Security. Включите их, прежде чем вернуться в Интернет.
Перепрошивка маршрутизатора
Ниже описаны три способа перепрошивки:
- Использование веб-интерфейса маршрутизатора,
- Использование TFTP. См. .
- Использование интерфейса командной строки (используйте его, если компьютер подключен к маршрутизатору по беспроводной сети). См. .
Используемый метод может зависеть от модели или местоположения маршрутизатора.
[edit] Introduction
This mode is NOT for WIRED connections between two routers, like an Access Point. It is a wireless connection between two routers only, usually to the primary gateway router. A Client Mode router connects to a Wireless Access Point (WAP) wireless connection as the WAN interface, and shares the internet connection only to the LAN ports, or a separate WAP for multi-radio routers. It is not seen as a WAP, nor accepts wireless connections by other client devices.
The primary (host) router is not required to be running DD-WRT firmware. The primary and secondary (DD-WRT Client Mode) routers must be on separate subnets, and NAT is used between them. Thus, when port forwarding is needed it must be configured at both routers — not just on the host router.
A Client Mode router uses its own DHCP server for IP Address, Gateway, and DNS server to connected devices. To have computers connected to both routers (main and secondary) and co-exist in the same subnet, set up DD-WRT as a Client Bridge, Repeater Bridge or use WDS. Further explanation of bridging modes is at Linking Routers.
If using a multi-band router, do not set more than one band to CB. The other radio(s) would normally be set as AP. For example, the 2.4GHz radio can a CB while the 5GHz is an AP, or vice versa.
[edit] Other Notes
Upgrading to a Newer Version of DD-WRT
If DD-WRT is already installed on your router, you can simply upgrade to a new version via the web interface or TFTP. However, it is highly recommended that you restore the router to defaults using the reset button before and after flash. Never restore old backups from previous versions! Skipping these steps could lead to a bricked device!
If you can’t wget the firmware
On routers without OpenSSL (e.g. 4MB models), the https link won’t work: use HTTP or FTP.
If you don’t ordinarily use DNSmasq for local DNS (perhaps because you run another DNS server), then the CLI commands may not be able to resolve addresses, so wget may fail. This can be hard to troubleshoot since the busybox commands don’t return errors. Possible workarounds:
Enable DNSmasq just while getting the file
nvram set dns_dnsmasq=1 stopservice dnsmasq startservice dnsmasq nvram set dns_dnsmasq=0
- Use nslookup on another host to get the IP address of ftp.dd-wrt.com, then download from
ftp://<ip>/<path>
Note: HTTP won’t work (the download1 vhost needs the «Host» header to give you the file, and the stripped-down DD-WRT wget doesn’t have the —header option).
Configuration Notes
You must start to configure router from scratch. Do not try to use config files from older firmware versions.
It is strongly advised that you do not disable the «Boot Wait» option under the «Administration» tab. Boot Wait allows you recover if you flash your router improperly.
[edit] Диагностика
Когда происходит такое замедление и маршрутизатор не отвечает ни на эхо-запросы команды ping, ни на запросы веб-интерфейса, вы всё равно можете проверить, что происходит:
- Закройте все P2P и сетевые приложения и подождите несколько минут, чтобы прекратить все соединения.
- Попробуйте использовать один из вариантов подключения к командной строке (SSH или Telnet) для связи с маршрутизатором.
- Если это невозможно, перезагрузите устройство DD-WRT.
- Проверьте, не вызвана ли ваша проблема соединениями TCP или UDP. Из командной строки:
cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/netfilter/ip_conntrack_max 4096 # Здесь маршрутизатор отображает максимальное количество возможных подключений. grep -c ^udp /proc/net/ip_conntrack 3693 # Открыто 3693 соединений по протоколу UDP grep -c ^tcp /proc/net/ip_conntrack 115 # Открыто 115 соединений по протоколу TCP
cat /var/log/messages
- Сначала вы увидите сообщения ‘full, dropping packet.’, следующие за ‘messages suppressed.’.
- В конце концов вы увидите журналы, подобные следующим:
<4>kernel: ip_conntrack: table full, dropping packet. <4>kernel: NET: 15 messages suppressed. <4>kernel: ip_conntrack: table full, dropping packet. <4>kernel: NET: 12 messages suppressed.
[edit] Способ 1: использование веб-интерфейса маршрутизатора
Сбросьте настройки маршрутизатора к завродским значениям.
Это, скорее всего, не потребуется, но если память или NVRAM маршрутизатора почти заполнены, обновление прошивки может привести к его повреждению. Таким образом, рекомендуется, по крайней мере, до подробного знакомства с конкретным устройством.
Выполните сброс в веб-интерфейсе (Administration → Factory Defaults в DD-WRT) или используйте альтернативный метод:
Сброс 30/30/30
Внимание: на некоторых устройствах нельзя использовать сброс 30/30/30, включая все устройства ARM.
Кнопка сброса Reset: при нормальном функционировании маршрутизатора удерживайте кнопку сброса до тех пор, пока индикаторы не начнут мигать (или до 30 секунд). Будьте осторожны при использовании этого метода! Изучите инструкцию к вашей текущей прошивке, чтобы избежать проблем.
Войдите в веб-интерфейс маршрутизатора.
Для нормальной работы веб-интерфейса может потребоватся Javascript
Попробуйте другой браузер при возникновении проблем.
Вам будет предложено ввести имя пользователя и пароль. Если ваш маршрутизатор уже имеет версию DD-WRT, начиная с 28 февраля 2006 г., имя пользователя по умолчанию — root. В предыдущих версиях по умолчанию используется пустое имя пользователя. Как для заводской, так и для прошивки DD-WRT маршрутизаторов Linksys имя пользователя по умолчанию можно оставить пустым или установить любое значение, а пароль по умолчанию — admin. Для других маршрутизаторов выполните поиск значений по умолчанию в Интернете.
Загрузите прошивку.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ. При перепрошивке с заводской прошивки может потребоваться несколько перепрошивок подряд. См. для дополнительной информации.
ВНИМАНИЕ: Не прерывайте процесс, пока маршрутизатор мигает и перезагружается. Не выключайте компьютер, не закрывайте браузер и не выключайте маршрутизатор во время этого процесса!
Этот раздел инструкции написан для веб-интерфейса DD-WRT. Интерфейс заводской прошивки будет другим. Смотрите раздел .
Перейдите на вкладку Administration → Firmware Upgrade.
Необязательно: выберите параметр Reset to Defaults, чтобы сбросить настройки к заводским значениям после перепрошивки (примечание: это может вызвать проблемы при перепрошивке).
Нажмите кнопку «Browse» и выберите загруженный бинарный файл .bin прошивки DD-WRT, контрольная сумма которого проверена.
Нажмите кнопку «Upgrade» и дождитесь появления страницы перенаправления, подтверждающей успешную загрузку.
Подождите не менее 5 минут, прежде чем нажать кнопку «Continue». Это зависит от оборудования маршрутизатора.
При успешной прошивке теперь можно получить доступ к веб-интерфейсу DD-WRT по IP-адресу 192.168.1.1.
Снова сбросьте настройки маршрутизатора к завродским значениям.
Делайте это только после того, как убедитесь, что маршрутизатор работает после обновления прошивки.
Это требуется при перепрошивке из заводской прошивки! Смотрите раздел выше.
В случае обновления версии DD-WRT это необходимо только при больших скачках в версии сборки, изменении версии ядра (например, с 2.4 на 2.6 или с 2.6 на 3.10) или при наличии проблем. Для последнего, сбросьте, повторно протестируйте, и затем ищите форум, прежде чем сделать новое сообщение.
Возможные ошибки при загрузке прошивки.
Если веб-интерфейс DD-WRT не доступен через 10 минут, попробуйте очистить кэш браузера, обновить IP-адрес («ipconfig -renew» в окне командной строки Windows), выполнить другой сброс или отключить питание.
Проверьте связь с маршрутизатором командой Ping: ответ TTL=64 указывает на нормальную работу, а TTL=100 обычно указывает на TFTP-сервер, ожидающий загрузки прошивки. Сервер TFTP, как правило, доступен только в первые пару секунд после включения питания. См. статью Tftp flash.
Процесс загрузки прошивки может завершится сообщением «Upload Failed» («Ошибка загрузки»), если используется неверный тип файла, ядро или размер бинарного файла прошивки DD-WRT (или может просто «превратиться кирпич»). Например, это может произойти, если вы используете файл wrt54g.bin тогда, когда вам нужно было выбрать generic версию. Также для некоторых маршрутизаторов может потребоватся, чтобы сборка Mini была перепрошита перед полной версией. Убедитесь, что у вас правильная версия, как описано в первом разделе.
См. статью Recover from a Bad Flash («Восстановление при неудачной перепрошивке») или попробуйте другой браузер для загрузки прошивки.
Если не удается выполнить вход в систему, используя имя пользователя и пароль по умолчанию, выполните сброс еще раз.
[edit] Roaming access
If you are installing additional Access Points to cover a broader area with Wi-Fi access, it is possible to allow clients to roam freely between them. The common method is to use the same SSID and Security settings on each access point. The clients control when to switch in between APs. Most clients will switch when they see a more powerful AP available but some client radios are not able to listen for a new AP when connected to an existing AP and as a result those clients will not roam to the new AP until they completely lose signal from the old one. A typical roaming transition from one AP to the other takes about 50ms if using simple authentication (open or WPA2 PSK AES)
Use a different channel on each AP. e.g. if you are in the US and installed two access points, use channels #1 and #11. Or if three access points, then use channels #1, #6, and #11 (setting the channels at least 5 apart should help keep interference between APs to a minimum). If you have a residential gateway with wireless turned on, and just one AP, then the same applies: each gets a different channel. If you are in Europe, use channels 1, 5, 9 & 13.
When using multiple Access Points, each one should be connected by LAN to LAN uplink as described above. They can even be attached to different switches within the same organization.
Access Point placements need to be carefully done. If the APs are too far away then there will be holes in the coverage and the clients will drop off when going from one AP to the other. If the APs are too close then clients will «stick» to one AP while moving out of its region and into another’s. If the APs are too close and moving them farther apart is not practical then the transmit power on each AP can be reduced.
You can also try setting the APs to use the same channel. This will halve bandwidth when both APs are talking to clients but it may help clients that have problems sticking to one AP.
It can also be helpful to disable the slower 802.11 transfer rates with the command for example:
wl down sleep 5 wl rateset 18b 24 36 48 54 wl up
This sets the minimum access to 18Mbit and clients will drop off as the signal level falls below what’s needed to support this.
There are additional considerations with roaming using wireless VoIP gear, and WPA Enterprise modes. These environments require additional authentication from the client that could exceed the TCP/IP TTL and cause a disconnection of a higher level application such as the VoIP client. Because of that, the IEEE 802.11r-2008 protocol, a.k.a. Fast Transition (FT), was developed. DD-WRT does not currently support 802.11r FT but there is support for it in OpenWRT. The wireless client must also support Fast Roaming for this protocol for it to work; typically it will be cell phones that support it.
[edit] Method 2: Flashing with TFTP
TFTP is generally a safe method to flash many routers. However, it is not preferred method for flashing most devices. In the Hardware-specific section you may be advised to use this method if it is the preferred or only method for your brand or type of device. Normally, the GUI flashing method should be used, as it is adequate for the vast majority of standard situations, but refer to the Hardware-specific section to be sure.
Tftp is easy: if often requires one quick box uncheck and a quick click — then you are good to go. It is great for instances when web GUI malfunctions or the router appears to be (but is not) bricked.
If you still wish to flash with TFTP, see the articles TFTP flash, Asus TFTP Flash and .
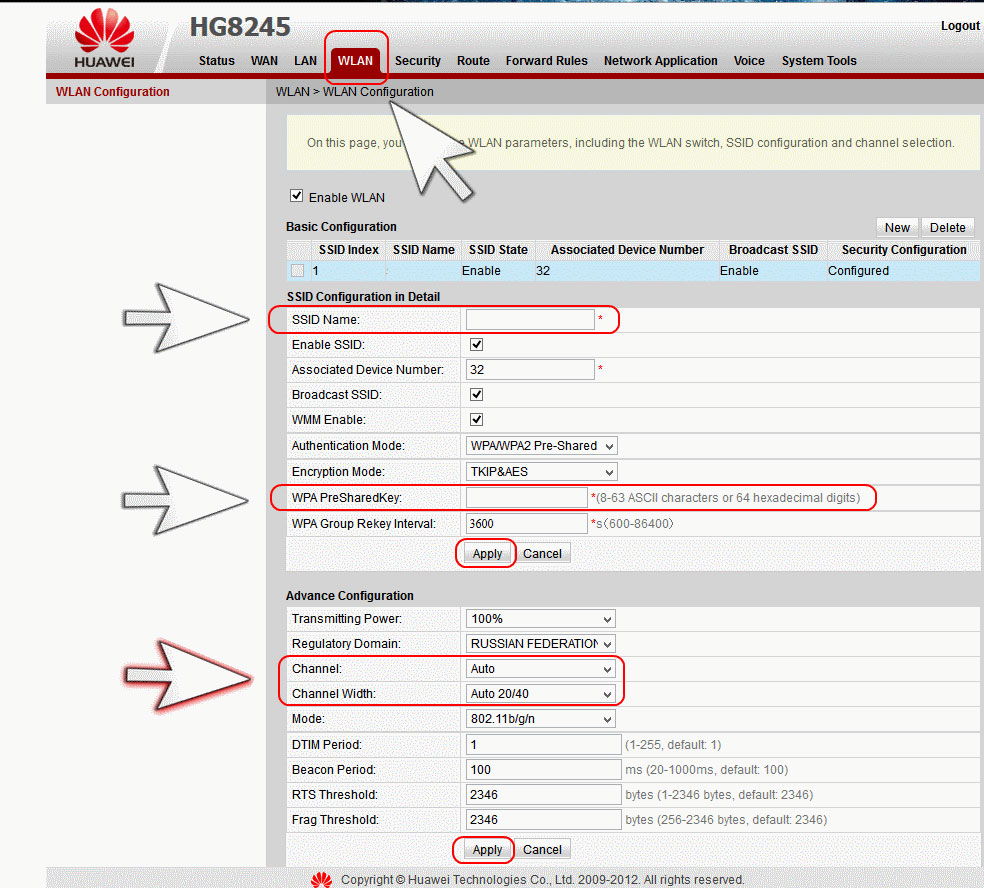
[edit] Какие настройки безопасности беспроводной сети следует использовать дома?
В домашней или небольшой офисной сети, вероятно, не будет RADIUS-сервера уровня предприятия, поэтому будет использоватся упрощённый режим персональных ключей Pre-Shared Key, который использует общую фразу-пароль для всех пользователей сети. WPA2 + AES — рекомендуемый выбор для домашних сетей.
См. .
Если в вашей сети есть RADIUS-сервер, лучше используйте его.
Фильтрацию MAC-адресов можно обойти путем клонирования MAC-адреса одного из устройств сети. Фильтрация MAC-адресов не заменяет шифрование, поскольку все данные передаются в открытом виде. Всегда используйте шифрование, когда это возможно.
Если вы используете GNU / Linux на своем ноутбуке, вы можете столкнуться с некоторыми проблемами с вашей беспроводной картой и шифрованием. Если проблема с обоими, просто поищите в Google хорошо поддерживаемый USB-адаптер беспроводной сети (с работающим WPA). Если единственной проблемой является WPA-шифрование, всегда есть (довольно сложный) запасной вариант использования OpenVPN для установления безопасного зашифрованного соединения.
Внешние ссылки
[edit] Приготовьтесь к автономной работе
- У вас не будет доступа в интернет через маршрутизатор во время замены прошивки. Вам придётся почти всё делать в автономном режиме, подключившись к маршрутизатору по локальной сети (не используя беспроводную сеть Wi-Fi, см. ). Учитывая множество проблем, с которыми вы можете столкнуться, попытка прошивки может завершится тем, что вы не сможете получить доступ в интернет и обратиться за помощью. Поэтому вам нужно будет заранее скачать на комьютер всё, что может понадобится, прежде чем начать. Это позволит просматривать информацию в автономном режиме в случае, если что-то пойдет не так.
- Пользователям Windows Vista на время перепрошивки рекомендуется отключить бесроводную сеть Wi-Fi на компьютере. См. .
- Запишите или сделайте снимок экрана текущих настроек маршрутизатора для дальнейшего использования. Среди настроек вам особенно могут понадобится:
- Имя пользователя и пароль для доступа в интернет, предоставленные интернет-провайдером.
- MAC-адрес маршрутизатора в глобальной сети WAN. Некоторые интернет-провайдеры не допускают немедленной смены оборудования без телефонного звонка. Поэтому после прошивки может понадобится выполнить настройку клонирования MAC-адреса.
- Статический IP-адрес, если используется.
- Во время экспериментов с прошивкой маршрутизатора рекомендуется иметь дополнительный способ доступа к Интернету, чтобы ускорить устранение неполадок в случае их появления.
- Рекомендуется сохранить информацию по следующим ссылкам на компьютер, чтобы иметь возможность просмотреть её в автономном режиме. Просто выберите в браузере меню Файл → Сохранить как.
- Страница модели вашего маршрутизатора в разделе Hardware-specific.
- Эта страница вики.
- Страница вики Recover from a Bad Flash, описывающая восстановление маршрутизатора после неудачной перепрошивки.
- Ответы на частозадаваемые вопросы Часто задаваемые вопросы.
- Кроме того, понадобится скачать следующие файлы:
- Первый бинарный файл «killer» для стирания заводской прошивки маршрутизатора. Может быть и не нужен, см. страницу вашей модели маршрутизатора в разделе Hardware-specific.
- Второй бинарный файл прошивки DD-WRT.
[edit] Other Notes
Upgrading to a Newer Version of DD-WRT
If DD-WRT is already installed on your router, you can simply upgrade to a new version via the web interface or TFTP. However, it is highly recommended that you restore the router to defaults using the reset button before and after flash. Never restore old backups from previous versions! Skipping these steps could lead to a bricked device!
If you can’t wget the firmware
On routers without OpenSSL (e.g. 4MB models), the https link won’t work: use HTTP or FTP.
If you don’t ordinarily use DNSmasq for local DNS (perhaps because you run another DNS server), then the CLI commands may not be able to resolve addresses, so wget may fail. This can be hard to troubleshoot since the busybox commands don’t return errors. Possible workarounds:
Enable DNSmasq just while getting the file
nvram set dns_dnsmasq=1 stopservice dnsmasq startservice dnsmasq nvram set dns_dnsmasq=0
- Use nslookup on another host to get the IP address of ftp.dd-wrt.com, then download from
ftp://<ip>/<path>
Note: HTTP won’t work (the download1 vhost needs the «Host» header to give you the file, and the stripped-down DD-WRT wget doesn’t have the —header option).
Configuration Notes
You must start to configure router from scratch. Do not try to use config files from older firmware versions.
It is strongly advised that you do not disable the «Boot Wait» option under the «Administration» tab. Boot Wait allows you recover if you flash your router improperly.